Western Nuclear, Inc. - Split Rock
1.0 General Site Information
| Site Location: |
Jeffery City, WY |
| Former NRC License No.: |
SUA-0056 |
| NRC Docket No.: |
400-1162 |
| Agreement State Contact: |
Brandi O’Brien |
307-777-6435 |
| NRC Agreement State Site Monitor: |
Duncan White |
Duncan.White@nrc.gov |
| NRC Site Monitor: |
Thomas Lancaster |
Thomas.Lancaster@nrc.gov |
2.0 Site Description
This is a uranium mill tailings site located approximately two miles northeast of Jeffrey City, Fremont County, Wyoming (Figure 1). The site is just south of the Sweetwater River. The site primarily consists of three reclaimed tailings impoundments occupying approximately 180 acres and other reclaimed disposal areas.
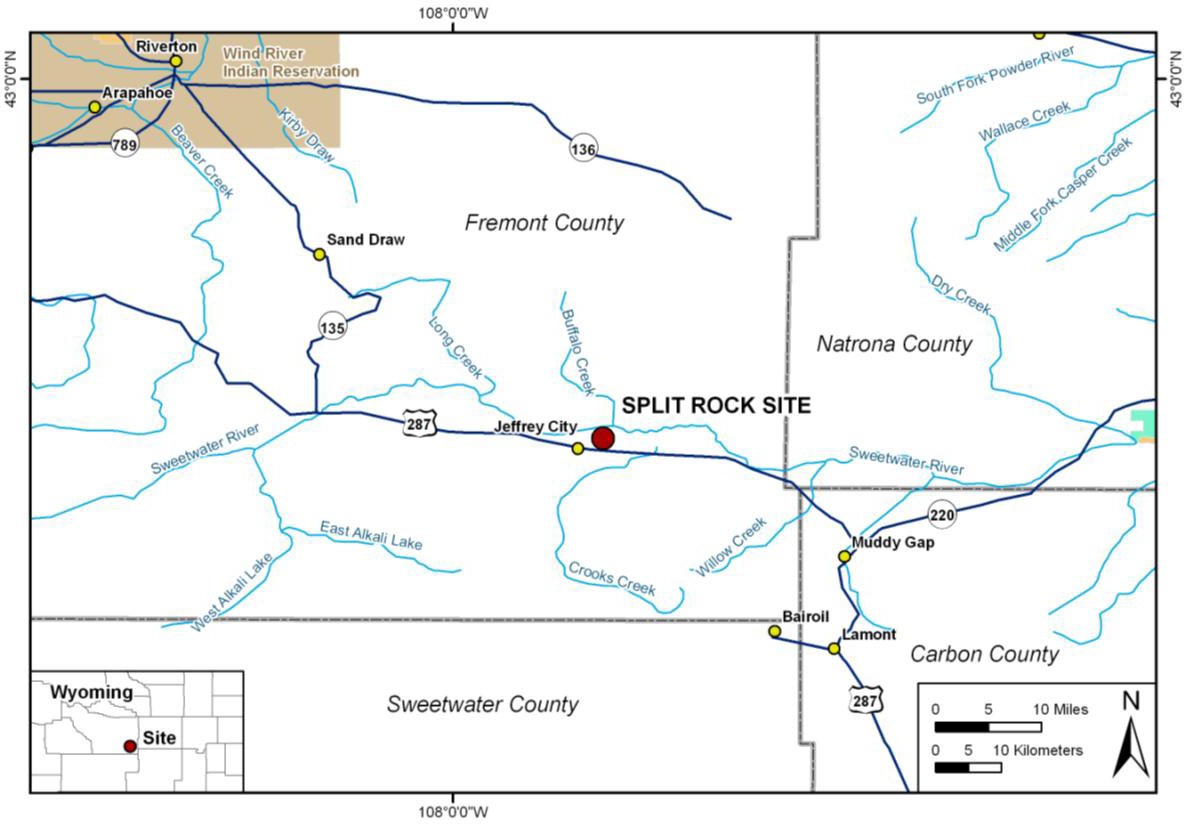
Figure 1. Split Rock Uranium Mill Site Location Map
3.0 Site History
Western Nuclear, Inc. (WNI) began construction of the Split Rock facility in 1956. Between 1957 and 1981, WNI used acid leach, ion exchange, and solvent extraction methods to process approximately 8 million tons of uranium ore from ore bodies north and south of the site. The mill was originally designed to process 400 tons of ore per day, but a series of expansions in the 1970s increased daily production to 1,700 tons. Three tailings disposal areas (the old, alternate, and new tailings impoundments) were used during mill operation (Figure 2). In June 1981, the mill was placed on standby due to declining uranium demand and prices. The mill remained on standby until 1986 when the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) amended the license to terminate the use of the tailings impoundments for disposal and WNI was required to submit a tailings reclamation plan. WNI completed decontamination and decommissioning of the mill in September 1988. Mill components were dismantled and buried beneath the former mill location. Surface reclamation for the tailings impoundments and the two evaporation ponds has been completed.
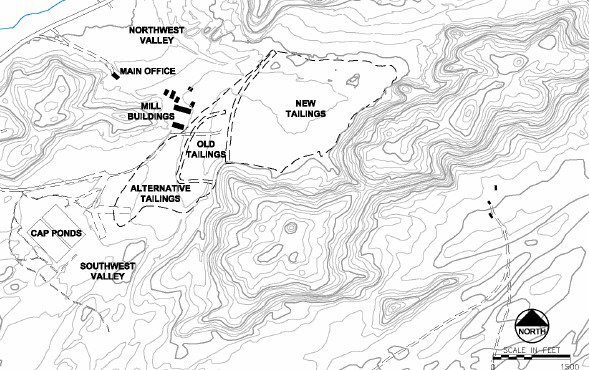
Figure 2. Split Rock Site Layout Source: U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. “Draft Environmental Assessment for Amendment to Source Material License SUA-56 for Ground Water Alternate Concentration Limits.” Washington, DC: U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. 2006.
The hydrogeological system beneath the former tailings impoundments comprises the Sweetwater River alluvium aquifer (also called the flood-plain aquifer) and the Split Rock aquifer. The 15-ft to 30-ft-thick flood-plain aquifer consists of river sediments that were formed where the Sweetwater River cut and meandered across the underlying Split Rock Formation. Both aquifers are hydraulically connected. The Split Rock Formation outcrops in a wedge-shaped pattern that begins approximately 20 miles west of the site and extends approximately 40 miles east of the site to the North Platte River. The formation covers approximately 1,500 square miles with a saturated thickness ranging from 500 to 3,000 feet south of the Sweetwater River and from 200 to 600 feet north of the river.
During operation of the Split Rock facility, WNI discharged process wastes into unlined tailings impoundments. Infiltration and seepage from these impoundments led to contamination of groundwater in the underlying aquifers and several corrective actions.
WNI began a corrective action program (CAP) in 1990, which involved extracting contaminated groundwater from the Northwest Valley and Southwest Valley areas to two lined evaporation ponds. In 1999, the groundwater cleanup goal was determined to be unachievable and the CAP was discontinued. Subsequently, institutional controls and groundwater alternate concentration limits (ACLs) were applied for and subsequently approved.
4.0 Current NRC actions/status
The Split Rock site is under regulatory review for the termination of the Western Nuclear, Inc. (WNI) Source Materials License SUA-0056 by the State of Wyoming and the transitioning of the site for long-term surveillance and care by the U. S. Department of Energy under an NRC general license.
5.0 Expected Transition to DOE for LTS&M
12/2022 (See DOE LM Site Management Guide, June 2022)
Page Last Reviewed/Updated Friday, October 28, 2022